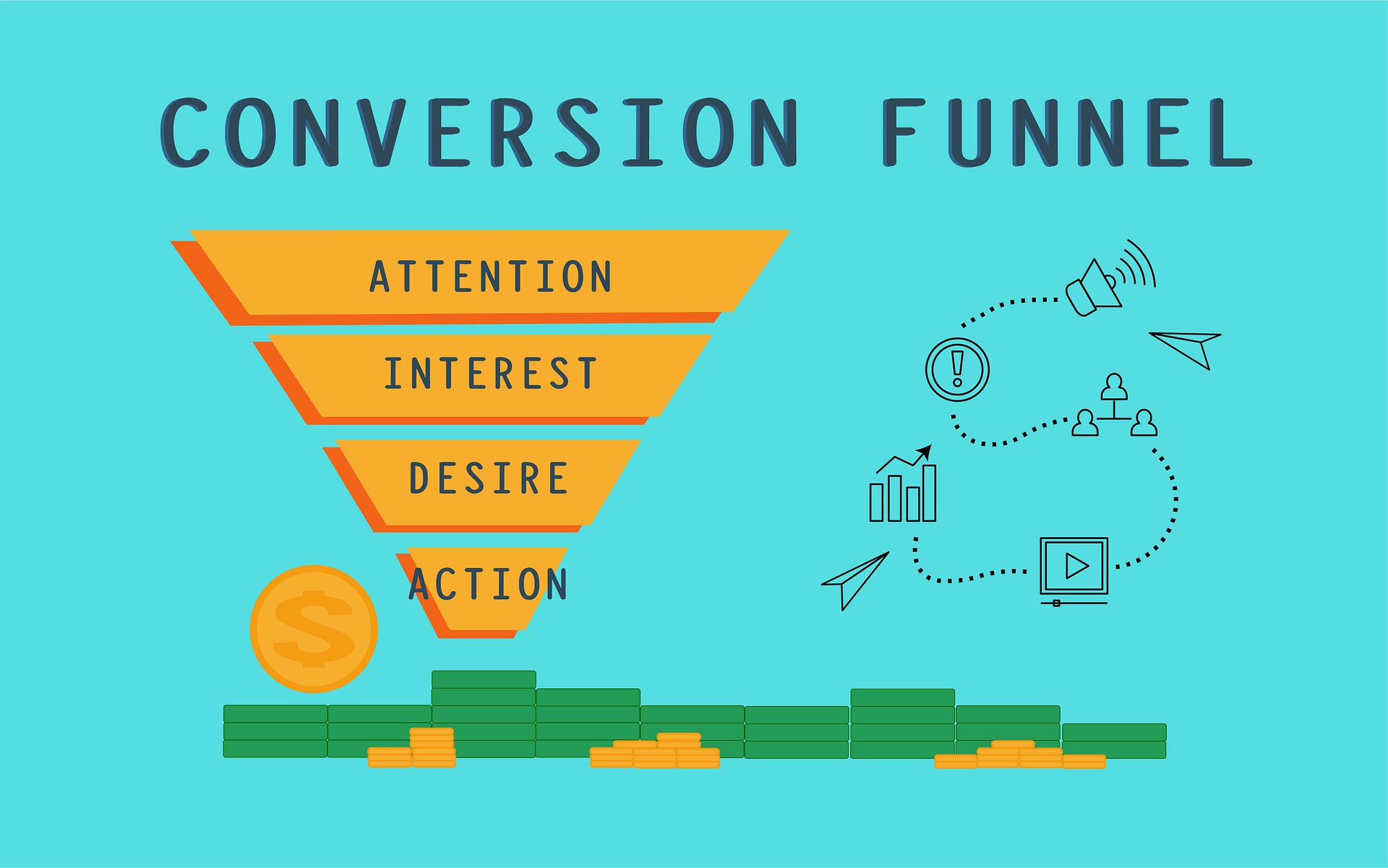
Definition and Importance
What is a Conversion?
- Understanding a Conversion
In digital marketing, a conversion refers to the process in which a prospect becomes a customer by completing a desired action. This could be filling out a contact form, subscribing to a newsletter, or purchasing a product. - Measurement and Importance of Conversion Rate
The conversion rate is a crucial metric that measures the percentage of conversions. It is calculated by dividing the number of completed activities by the total number of visitors. This rate is a central indicator of success and helps track progress towards specific goals. - Diversity of Conversion ActionsConversions can be achieved through various actions, including purchases, newsletter sign-ups, form submissions, or downloads. Each of these actions contributes to measuring the effectiveness of your online marketing strategies.
- Importance of Conversion for Online MarketingConversions are scalable metrics for success measurement in online marketing, which are highly important for website operators, advertisers, and agencies. They enable an accurate evaluation of the effectiveness of the implemented marketing strategies.
- Awareness of Manipulation Possibilities
It is essential to be aware of potential manipulation of conversions, especially with downloads or newsletter registrations. Website operators should control the customer journey and the sources leading to a conversion to ensure accurate and authentic data.
Types of Conversions
Types of Conversions
1. Classic “Hard Conversions”
Hard conversions are directly related to purchase decisions. Examples include:
- Signing up for a product demonstration
- Specific contact inquiries
- Orders or purchases
This type of conversion is crucial because it directly leads to revenue and is thus easily quantifiable.
2. “Soft Conversions”
Soft conversions are less direct but equally important, as they indicate interest in your company. Examples include:
- Newsletter sign-ups
- Downloads of informational material such as whitepapers or e-books
These conversions are often preliminary stages to a later purchase decision and help identify and engage potential customers.
3. Additional Important Conversion Types
Besides the classic conversions, there are other important actions that can be considered conversions:
- Submission of a contact form
- Registration in a forum or community
- Clicking on a link or advertisement
- Sharing content on social networks
Each of these actions contributes to strengthening the bond between you and your visitors and can ultimately lead to a purchase decision.
These different types of conversions illustrate that the conversion process is multifaceted and extends beyond mere contact acquisition. It is important to recognize and promote all forms of conversions to successfully implement a comprehensive strategy in online marketing.
Measuring Conversions
To effectively measure your conversion rates, the use of specialized tools like Google Analytics is essential. These systems enable you to precisely track and analyze conversions to evaluate the effectiveness of your online marketing campaigns. You can also create your own conversion definitions in Google Ads to specifically measure the success of your search engine advertising (SEA).
Primary and Secondary Metrics
Primary Metrics
- Number of Conversions: Measures the total number of desired actions completed.
- Conversion-Rate (CVR): Calculated as (Number of Conversions / Total Number of Visitors) * 100.
- CPA (Cost per Action): The cost incurred to achieve a conversion.
- ROI (Return on Investment): Measures the profitability of the invested funds.
- ROAS (Return on Advertising Spending): Indicates how effective your advertising spending is.
Secondary Metrics
- Visitors: Total number of visits to your website.
- Unique Visits: Number of unique visitors.
- Returning Visitors: People who visit your website multiple times.
- Page-Impressions: Number of page views.
- Bounce Rate: Percentage of visitors who leave the site without taking further actions.
- Duration of Visit: Average time visitors spend on your website.
- CTR (Click-Through-Rate): Ratio of clicks to impressions in advertisements.
Influencing Factors and Optimization
The conversion rate is not only determined by the number of visitors but also by factors such as web design, visitor source, pricing, market environment, and competition. A more in-depth analysis of these factors can help you identify areas where optimizations are possible to maximize not only the conversion rate but also make it more effective.
By regularly analyzing these metrics and pursuing relevant goals, you can develop a better understanding of your users’ behavior and adapt your online marketing strategies accordingly.

Factors Influencing Conversions
Permanent and Temporary Factors
Permanent Factors
- Current Trends: Adapt to seasonal or event-related fluctuations in customer interest and buying behavior.
- Technological Developments: Update to mobile-friendly websites and modern payment methods.
- Economic Changes: Respond to economic fluctuations with attractive promotions or discounts.
- Legal and Environmental Changes: Stay informed about legal and ecological changes that could affect your business.
- Market Changes: Observe market developments, such as expansions or closures, and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Changes in Target Audience Behavior: Understand and adapt to changes in the preferences and characteristics of your target audience.
Temporary Factors
- Website Visitor Numbers: Analyze visitor numbers to optimize marketing strategies and resource allocation.
- Competitiveness: Adapt to competitors’ strategies and offer unique value propositions.
- Product Offerings: Simplify the purchasing process and use search filters and sorting tools to improve user experience.
- Marketing Strategies: Utilize all available channels to promote your website and increase conversions.
External Factors
- Unexpected External Influences: Weather conditions, seasonal influences, economic conditions, competitor actions, unexpected events, political decisions, and specific periods like the beginning or end of a month can significantly impact conversion rates.
SEO and Conversion Optimization
Search engine optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role, as websites that rank well organically have higher chances of conversions through increased traffic. Regular analyses of website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates are essential for successful conversion rate optimization (CRO). Testing is a critical component of CRO, and it is advisable to test different versions of your website to determine the most effective one.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) Steps
To optimize your conversion rate (CRO), follow these steps:
- Assess your CRO status quo::
Understand the current state of your website concerning conversion rate. Analyze existing data and track user interactions to identify areas that can be improved.
- Set goals and form hypotheses:
Set clear goals for optimization and develop hypotheses about how changes on your website could influence the conversion rate. Base these hypotheses on collected data and your knowledge of the target audience.
- Understand your target audience:
Gain a deep understanding of your target audience to recognize their needs and desires. This helps in designing a user-friendly website that encourages conversion.
- Develop a CRO strategy:
Plan a comprehensive strategy based on the previous steps. This includes optimizing layout, content, and call-to-action elements to improve user experience and increase conversion rate.
- Implement and test:
Implement the planned changes and conduct A/B tests to compare the effectiveness of different website versions. This allows you to make data-driven decisions about the most effective elements.
- Evaluate and optimize:
Analyze the test results and make further adjustments to continuously improve the conversion rate. Consider this process an ongoing task to achieve optimal results.
- Scale and continuously improve:
After successful tests and optimizations, apply proven strategies to other areas of your online presence. Simultaneously, integrate new trends and technologies to keep optimizing the conversion rate and meet the changing requirements of users.
Branding and advertising
Future of Conversion Tracking
Adaptations and Challenges
- Regular updates: To continuously optimize the effectiveness and ROI of your marketing campaigns, regular updates in conversion tracking are essential. These adaptations help you adjust to dynamic market conditions and refine your strategies accordingly.
- Diversity of technologies: The fragmentation and diversity of devices, browsers, operating systems, and apps pose a challenge for conversion tracking. It is crucial that your tracking tools can effectively manage this variety to collect accurate data.
- Data privacy and security: Given the growing concerns about data privacy and security, particularly regarding the use of cookies and trackers, you must ensure that your tracking methods comply with data protection authorities’ regulations such as the GDPR and the CCPA.
Advanced Tracking Methods
- Server-side tracking: This method bypasses the limitations of client-side tracking by sending data directly from the server to the analytics platform, improving data accuracy and reducing privacy concerns.
- Consent management: Managing consent for data usage is essential to meet legal requirements, ensuring that data processing is transparent and conducted with users’ consent.
- Cross-Device and cross-platform tracking: These techniques connect user behavior and conversions across multiple devices and platforms, providing a consistent and seamless experience for users.
Use of AI and Machine Learning
- Machine learning and AI: The application of advanced algorithms and models enables learning from collected data and gaining valuable insights, predictions, and recommendations for conversion tracking and optimization.
New Developments in Analytics Tools
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4): With features like Enhanced Conversion, which allows enriching conversion data with additional information, and Consent Mode V2, which provides more precise control over data usage and ensures GDPR compliance, GA4 represents a significant development.
- Server-side tracking with Google Tag Manager (GTM): In the EEA, server-side tracking is gaining importance for effective remarketing and retargeting.
Future Updates and Trends
- Privacy protection: Future updates and trends in digital analytics will increasingly focus on privacy-compliant solutions to meet evolving legal requirements.
- Conversion rate in Google Ads:Measuring the conversion rate through Google Ads, calculated by dividing the number of conversions by the total number of ad clicks within a specific time frame, remains a central aspect of conversion tracking.
FAQs
What is the principle of a conversion in online marketing? A conversion in online marketing refers to the transformation of a prospect into a customer. The term “conversion” or “konversion” stands for “conversion.” This occurs when a person performs a specific action desired by the company, such as making a purchase.
Can you explain the conversion rate in simple terms? The conversion rate, often abbreviated as CVR, measures the ratio between the number of visitors to a website and the number of those who perform a desired action (conversion). For example, if 10 out of 1,000 website visitors buy a product, the conversion rate is 1%.
What is considered a good conversion rate for an online shop? For online shops, a good conversion rate from website visits to leads (prospects) is considered to be between 1 and 5 percent. The conversion rate from leads to actual customers should be between 1 and 20 percent.
How is conversion tracking carried out? Conversion tracking is a free process that records what happens after a customer interacts with your ads. It allows you to determine whether the customer made a purchase, signed up for the newsletter, contacted your company, or downloaded your app.